Did you know that the number of people worldwide living with diabetes is predicted to reach a staggering 783 million by 2045? Diabetes is a global epidemic that affects millions of individuals and their communities, posing significant challenges to healthcare systems and individuals alike.
Key Takeaways:
- Diabetes is a chronic condition with a rising prevalence worldwide.
- The number of people with diabetes is expected to reach 783 million by 2045.
- Various factors contribute to the increasing diabetes rates, including lifestyle factors and socioeconomic development.
- Managing diabetes on a global scale requires access to care, education, and effective management strategies.
- Prevention efforts, such as maintaining a healthy weight and following a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Global Diabetes Prevalence
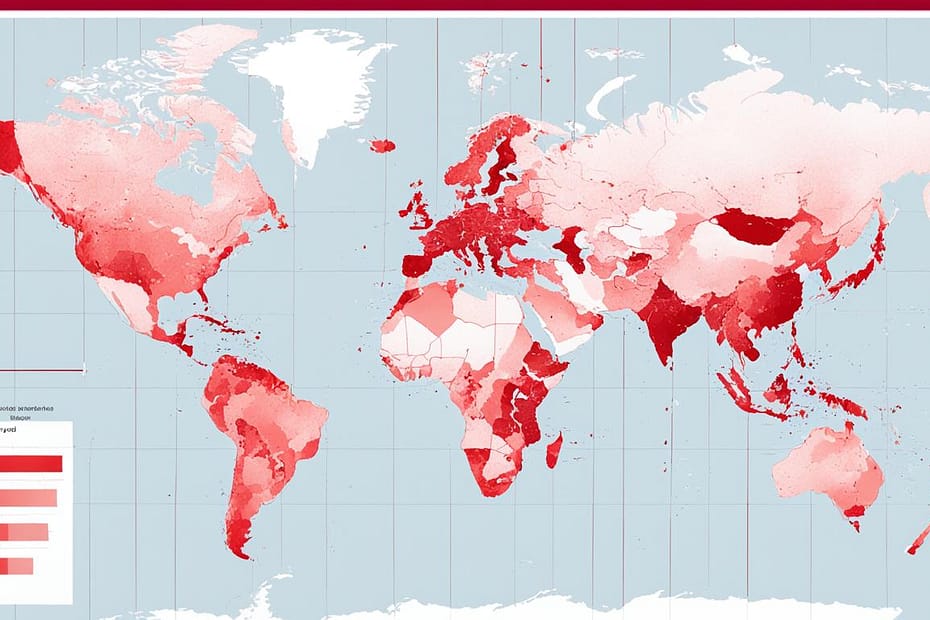
The prevalence of diabetes varies by country, with some nations experiencing higher rates than others. According to data from the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), Pakistan, French Polynesia, and Kuwait have the highest estimated prevalence rates of diabetes. In Pakistan, the prevalence is at a staggering 30.8%, while in French Polynesia and Kuwait, it stands at 25.2% and 24.9% respectively. These countries are projected to maintain the highest comparative diabetes prevalence rates in 2045.
When looking specifically at type 1 diabetes in children, the United States has the highest number of cases per 1,000 people. This is followed by India and Brazil, which also face significant challenges in managing diabetes among their youth. On the other hand, China has the largest number of adults living with diabetes, followed closely by India and Pakistan. These statistics highlight the global nature of the diabetes crisis, affecting people of all ages and from all corners of the world.
Understanding the global prevalence of diabetes is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat this chronic condition. By analyzing diabetes rates in different countries, health organizations and policymakers can identify hotspots and allocate resources accordingly, focusing on prevention, education, and access to quality healthcare. By addressing the underlying causes, raising awareness, and implementing evidence-based interventions, we can collectively work towards reducing the global burden of diabetes.
Rising Global Diabetes Rates
The prevalence of diabetes is on the rise globally, with an alarming increase predicted by 2045. According to studies, it is estimated that there will be a 46% increase in diabetes rates worldwide. This rise in diabetes prevalence has led to what can be described as a global diabetes epidemic, demanding immediate attention and efforts to combat this growing health concern.
Several factors contribute to the rise in diabetes rates. Aging populations in many countries play a significant role in this increase. As individuals grow older, the risk of developing diabetes also increases. Additionally, economic development and increasing urbanization have contributed to rising rates of diabetes. Urban areas often have environments that promote sedentary lifestyles and easy access to highly processed, unhealthy foods. This combination of factors has led to an increase in obesity rates, which is strongly linked to the development of type 2 diabetes.
However, it is important to note that not all cases of rising diabetes rates can be solely attributed to these factors. Other factors such as early detection, effective treatment, and improved survival rates also contribute to the overall increase in diabetes prevalence. Advancements in healthcare and better access to diabetes screenings have resulted in more individuals being diagnosed with diabetes, leading to a higher reported prevalence.
It is crucial for public health organizations and governments to address these rising diabetes rates. Strategies that focus on prevention, early detection, and providing comprehensive healthcare are essential in tackling this global diabetes epidemic. By promoting healthy lifestyle choices, raising awareness about diabetes, and implementing effective prevention programs, we can work towards reducing the burden of diabetes on individuals and healthcare systems worldwide.
Impact of Lifestyle on Diabetes Rates
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in the development and prevention of diabetes. Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle are known risk factors that significantly contribute to the increasing diabetes rates worldwide. It is important to understand the impact of these lifestyle factors and adopt healthy habits to combat this chronic condition.
One of the key lifestyle factors linked to diabetes is obesity. **Obesity** is defined as having an excessive amount of body fat, and it greatly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.**^1^** Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential for diabetes prevention.
A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of sitting or physical inactivity, is another lifestyle factor that has been strongly associated with the development of diabetes. Research has shown that being physically active can **lower the risk of diabetes** by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing body weight. Regular exercise, such as **aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity five days a week**, can have a significant impact on diabetes prevention.**^2^**
“Physical activity is one of the best ways to prevent and manage diabetes. It not only helps in maintaining a healthy weight but also improves overall health and well-being.” – Dr. Rachel Pearson**^3^**
Eating a healthy diet is also essential in preventing diabetes. **A well-balanced diet** that includes **fruits, vegetables, lean meats, whole grains, and foods high in unsaturated fats** not only helps in maintaining a healthy weight but also provides essential nutrients that support overall health. Controlling portion sizes and avoiding foods high in saturated and trans fats can also contribute to diabetes prevention.
“Following a healthy diet is a cornerstone of diabetes prevention. By choosing nutritious foods and adopting a balanced eating pattern, we can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.” – Lisa Taylor, Registered Dietitian**^4^**
In summary, lifestyle factors such as obesity and a sedentary lifestyle have a significant impact on diabetes rates. By maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, and following a balanced diet, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Taking proactive steps towards a healthier lifestyle is key to diabetes prevention and overall well-being.
References:
- NHS Choices. (2018). Causes of type 2 diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/type-2-diabetes/causes/
- American Diabetes Association. (2021). Exercise Can Help Manage Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/fitness/get-started-safely/exercise-can-help-manage-diabetes
- Pearson, R. (2019). The Role of Physical Activity in Diabetes Management. Diabetes Forecast. Retrieved from https://www.diabetesforecast.org/lifestyle/the-role-of-physical-activity-in-diabetes-management.html
- Taylor, L. (2021). Eating well with diabetes. EatRight Ontario. Retrieved from https://www.eatrightontario.ca/en/Common-Questions/Diabetes/Eating-well-with-diabetes.aspx
Managing Diabetes on a Global Scale
Managing diabetes on a global scale requires a comprehensive approach that includes accessible diabetes care, increased awareness about the condition, and the implementation of effective management strategies. By addressing these key areas, we can make significant progress in combating the global diabetes epidemic and improving the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
Diabetes Management Strategies
Effective diabetes management strategies encompass a range of interventions, including lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. These strategies aim to control blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and improve overall health. It is crucial to develop and implement evidence-based guidelines that provide clear direction on the best practices for diabetes management.
Access to Diabetes Care
Access to quality diabetes care is essential for individuals living with diabetes to effectively manage their condition. This includes access to healthcare professionals specialized in diabetes, such as endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and dietitians. Governments and healthcare systems need to prioritize investment in diabetes care infrastructure, ensuring that it is accessible and affordable for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Diabetes Education and Awareness
Education plays a pivotal role in empowering individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to manage their diabetes effectively. Diabetes education programs should be accessible and tailored to the specific needs of different populations, considering factors such as age, cultural background, and socioeconomic status. Increased awareness campaigns are also crucial in disseminating accurate information, challenging stigmas, and promoting early diagnosis and intervention.
“Diabetes education is a cornerstone of successful diabetes management. By equipping individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills, we empower them to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their diabetes care.”
Healthcare Systems and Diabetes
A well-functioning healthcare system is vital for managing diabetes on a global scale. This includes comprehensive healthcare coverage that encompasses diabetes prevention, screening, diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management. Healthcare systems should allocate resources for diabetes prevention and management programs, establish diabetes clinics or centers of excellence, and integrate diabetes care into primary healthcare services. Collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations is crucial in developing and implementing effective strategies to address the unique challenges posed by diabetes.
By prioritizing accessible diabetes care, raising awareness about diabetes, and implementing effective management strategies, we can enhance diabetes management on a global scale, improve health outcomes, and reduce the burden of this chronic condition. It is crucial for individuals, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and various stakeholders to work together to create a world where diabetes is effectively managed, and everyone has the opportunity to live a healthy life.
Diabetes Rates in Different Regions
The prevalence of diabetes varies by region, with different parts of the world experiencing different rates of diabetes. Africa currently has the lowest prevalence of diabetes, with a rate of 4.5%. However, this number is expected to increase significantly in the coming years. By 2045, it is predicted that 55 million people in Africa will be living with diabetes, marking a 129% increase from the current prevalence.
In 2021, the Middle East and North Africa region had the highest comparative prevalence rates of diabetes at 18.1%. This region faces significant challenges in managing diabetes, with factors such as genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and limited access to healthcare contributing to the high rates. On the other hand, North America and the Caribbean have the lowest comparative prevalence rates at 10.8%. These regions have implemented effective strategies for diabetes prevention and management, resulting in lower overall prevalence rates.
To visualize the diabetes rates in different regions, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Region | Diabetes Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Africa | 4.5% |
| Asia | 9.1% |
| Europe | 10.3% |
| North America | 10.8% |
| South America | 11.8% |
This table displays the prevalence of diabetes in various regions, providing a clear comparison of rates. While Africa has the lowest prevalence, Asia, Europe, and South America have slightly higher rates. It is essential to focus on preventive measures, access to healthcare, and education in regions with higher prevalence to curb the growing diabetes epidemic.
In conclusion, understanding the regional differences in diabetes rates is crucial for developing targeted prevention and management strategies. By analyzing these rates and implementing effective interventions, we can work towards reducing the burden of diabetes worldwide.
Undiagnosed Diabetes
Undiagnosed diabetes remains a significant challenge in healthcare systems worldwide, with almost one-in-two adults living with diabetes unaware of their condition. An estimated 240 million people, equivalent to the population of a large country, are living with undiagnosed diabetes globally. The lack of diabetes diagnosis is particularly prevalent in low-income countries, where the highest proportion of undiagnosed cases can be found.
In regions such as Africa, the Western Pacific, and South-East Asia, more than half of people with diabetes have not been diagnosed. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for effective screening strategies to identify undiagnosed diabetes and provide timely interventions.
Screening strategies play a crucial role in detecting undiagnosed diabetes cases. Diabetes risk scores, which evaluate factors such as age, body mass index, family history, and blood pressure, can help identify individuals at high risk. In addition, diagnostic tests such as fasting plasma glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) can confirm the presence of diabetes. Implementing these screening strategies is essential to expand preventive counseling and clinical care for undiagnosed individuals.
“Early detection is key to preventing the complications associated with undiagnosed diabetes.”
Expanding Diabetes Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about the importance of diabetes screening and diagnosis is crucial in addressing the issue of undiagnosed diabetes. Public health campaigns, educational initiatives, and community outreach programs can help individuals understand the risks, symptoms, and consequences of diabetes. By promoting diabetes education and expanding public knowledge, we can encourage more people to seek testing and receive the necessary care.
The Role of Healthcare Systems
The burden of undiagnosed diabetes can be reduced through improvements in healthcare systems. Integrated approaches that prioritize diabetes education and awareness help ensure that healthcare providers and individuals are equipped with the knowledge and resources needed for early detection and appropriate management. By fostering a patient-centered approach and ensuring access to affordable screening and diagnostic services, healthcare systems can make significant progress in reducing undiagnosed diabetes rates.
The Impact of Addressing Undiagnosed Diabetes
Efforts to identify and diagnose undiagnosed diabetes cases offer numerous benefits. Early detection allows individuals to receive appropriate treatment and lifestyle interventions, reducing the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes. This, in turn, leads to improved health outcomes, better quality of life, and reduced healthcare costs. By addressing undiagnosed diabetes, we can make significant strides towards achieving a healthier population and mitigating the burden of this chronic condition worldwide.
Future Projections for Diabetes Rates
As we examine future trends in diabetes prevalence, it becomes evident that the global burden of this chronic condition will only continue to rise. By 2030, an estimated 643 million adults aged 20-79 years will be living with diabetes, a staggering number that is projected to increase to 783 million by 2045.
This significant increase in projected diabetes rates is a cause for concern, particularly in middle-income countries where aging populations contribute to the greatest prevalence. These countries face unique challenges in managing diabetes on a larger scale, necessitating the development and implementation of effective strategies to address this public health crisis.
Predicted Diabetes Prevalence by 2030:
| Country | Diabetes Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|
| China | 12.8 |
| India | 9.8 |
| United States | 10.9 |
| Brazil | 10.0 |
These projections highlight the urgent need for comprehensive diabetes management and prevention strategies. As the global diabetes epidemic continues to unfold, it is essential that governments, healthcare systems, and communities prioritize education, access to care, and lifestyle interventions to curb the rising prevalence of this debilitating condition.
By understanding the projected diabetes rates, we can proactively address this challenge and work towards a healthier future where diabetes is better managed and prevented on a global scale.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global diabetes rates are on the rise, impacting countries differently based on various factors. Lifestyle choices, particularly obesity and sedentary behavior, contribute significantly to the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide.
To address this growing health concern, it is crucial to implement effective diabetes management strategies, improve access to care and education, and launch awareness campaigns. Governments and healthcare systems play a pivotal role in enacting policies and allocating resources to prevent and manage diabetes effectively.
Early detection, proper management, and lifestyle changes are key in mitigating the impact of diabetes. By prioritizing proactive measures and empowering individuals to make healthier choices, we can collectively combat the global diabetes epidemic and improve the lives of millions affected by this chronic condition.