Did you know that diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of vision loss among people with diabetes?
Diabetic retinopathy is a retinal disease and one of the most common and serious diabetes-related eye complications. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, this damage can lead to vision loss or even blindness if not detected and treated early.
Key Takeaways:
- Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive eye disease caused by high blood sugar levels.
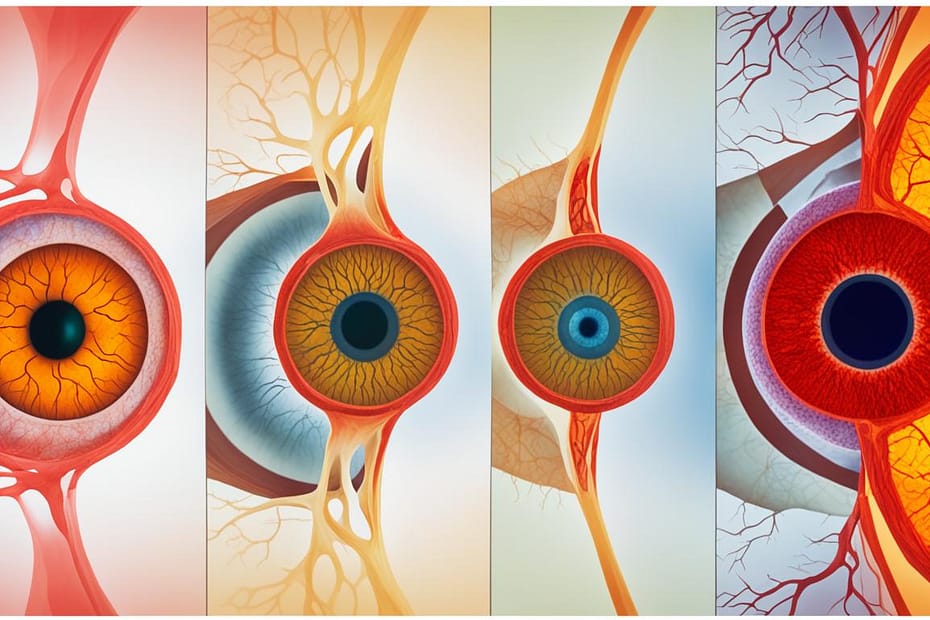
- The disease progresses through four stages: mild nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Regular eye exams and early detection are crucial in managing diabetic retinopathy and preventing vision loss.
- Treatment options for diabetic retinopathy vary depending on the stage and may include blood sugar management, eye injections, laser surgery, and vitrectomy.
- Preventive screenings and proper management of diabetes can help reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
What Are the Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy progresses through four stages. It is important to understand these stages to effectively manage the disease. Let’s take a closer look at each stage:
Mild Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
The first stage of diabetic retinopathy is mild nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (mild NPDR). In this stage, tiny swellings called microaneurysms develop in the blood vessels of the retina. Although it may not cause noticeable symptoms, early detection is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
Moderate Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
In the second stage, known as moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (moderate NPDR), the blood vessels in the retina continue to swell. This swelling can lead to blurry vision and affect overall visual acuity. Regular eye exams are essential during this stage to monitor the progression of the disease.
Severe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
As diabetic retinopathy advances to severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (severe NPDR), a larger portion of the blood vessels become blocked. This can result in blurry vision, the appearance of dark spots, and patches of vision loss. Timely treatment is vital to prevent permanent damage to the retina.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
The final stage of diabetic retinopathy is proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). In this stage, new abnormal blood vessels start to grow in the retina. These vessels are fragile and prone to leaking, potentially leading to retinal detachment and severe vision loss or blindness. Immediate medical intervention is necessary to save vision and preserve overall eye health.
Understanding the stages of diabetic retinopathy is crucial for early detection and effective management. Regular eye exams, proper blood sugar control, and prompt medical intervention can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss associated with this progressive eye disease.
Common Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive condition that typically does not present obvious symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease advances, individuals may experience a range of symptoms that indicate the presence of diabetic retinopathy.
One of the most common symptoms is blurry vision, which can make it difficult to focus clearly on objects. Changes in colors may also occur, with some individuals noticing a shift in their ability to perceive colors accurately. Moreover, a decrease in the field of vision can be observed, limiting the range of what can be seen within the visual field.
Distorted vision is another symptom of diabetic retinopathy, whereby straight lines may appear bent or wavy. Additionally, eye floaters, which are tiny specks or strings that float across the visual field, may become more noticeable.
As the condition progresses, individuals may experience a loss of vision, which can range from partial to complete vision loss in severe cases. Furthermore, poor night vision, making it challenging to see in dimly lit environments, is another symptom that can be indicative of diabetic retinopathy.
It’s important to note that symptoms of diabetic retinopathy typically occur when the disease has already reached an advanced stage. This highlights the critical importance of regular eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy early, before irreversible damage occurs.
To provide a visual representation of the common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy, please refer to the diagram below:
As shown in the diagram, the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy can significantly impact an individual’s vision and overall quality of life. It is essential to be vigilant and seek prompt medical attention if any of these symptoms are experienced.
How to Treat Diabetic Retinopathy
When it comes to treating diabetic retinopathy, the approach varies depending on the stage and severity of the disease. The key goals of treatment are to manage blood sugar levels effectively, prevent further vision loss, and address any complications that may have arisen.
For individuals in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, treatment may primarily focus on blood sugar management through a combination of diet, regular physical activity, and diabetes medication. By keeping blood sugar levels within the target range, the progression of the disease can be slowed down, reducing the risk of vision loss.
In cases where diabetic retinopathy has advanced to mild or moderate stages, additional treatment options may be necessary. One common approach is the use of eye injections, which involve the administration of medications directly into the eye to reduce inflammation and swelling. This can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage to the retina.
Another treatment option is laser surgery, which is performed to reduce swelling in the retina. The laser is used to target and seal off leaking blood vessels, as well as to shrink abnormal blood vessels. This procedure can help improve vision and prevent complications associated with diabetic retinopathy.
In more severe cases, where there is extensive retinal damage or detachment, a vitrectomy may be required. This surgical procedure involves removing blood or fluid from the eye and correcting any retinal detachment. By restoring the integrity of the retina, vision can be significantly improved.
It’s important to note that diabetic retinopathy is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and regular monitoring. Timely intervention and close collaboration with healthcare professionals are crucial for effective treatment and optimal outcomes.
By following a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses blood sugar management, utilizes appropriate interventions such as eye injections or laser surgery when necessary, as well as regular check-ups for monitoring progress, individuals with diabetic retinopathy can help preserve their vision and maintain optimal eye health.
Who is At Risk for Diabetic Retinopathy?
Individuals with diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes, are at risk for developing diabetic retinopathy. The longer someone has had diabetes, the higher their risk of developing this eye disease.
Studies have shown that nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, the early stage of the disease, can be present in a significant percentage of patients within 5 to 15 years of being diagnosed with diabetes. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with diabetes to undergo regular eye exams to detect and manage diabetic retinopathy in its early stages.
| Type of Diabetes | Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy |
|---|---|
| Type 1 diabetes | Increased risk |
| Type 2 diabetes | Increased risk |
| Gestational diabetes | Increased risk during and after pregnancy |
Regular eye exams play a vital role in identifying diabetic retinopathy at its earliest stages, allowing for timely intervention and effective management. By monitoring the retinal health of individuals with diabetes, healthcare providers can help prevent vision loss and ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
Remember, early detection is key in protecting your vision and managing diabetic retinopathy.
The Four Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive disease that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. It advances through four stages, each representing the progression of the disease and carrying an increasing risk of vision loss. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the disease and preventing irreversible damage.
Mild Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (mild NPDR)
In this initial stage, known as mild NPDR, small swellings called microaneurysms develop in the blood vessels of the retina. Although symptoms may be absent or minimal at this stage, regular monitoring is essential to detect any progression.
Moderate Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (moderate NPDR)
The second stage, moderate NPDR, is characterized by further swelling of the blood vessels, leading to blurry vision. Other symptoms may also become noticeable at this stage, indicating the need for early intervention and appropriate treatment.
Severe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (severe NPDR)
As the disease progresses to severe NPDR, a larger portion of blood vessels becomes blocked, resulting in more pronounced vision problems. Symptoms may include blurry vision, dark spots, and patches of vision loss. Close monitoring and prompt treatment are crucial at this stage to prevent further damage.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
The final and most advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy is proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). At this stage, new and abnormal blood vessels develop in the retina, increasing the risk of retinal detachment and permanent vision loss. Timely and comprehensive treatment options, including blood sugar management, eye injections, laser surgery, and vitrectomy, are essential to preserve vision and minimize the impact of the disease.
“The four stages of diabetic retinopathy illustrate the progressive nature of the disease. Early detection and intervention are key to managing the disease effectively and preserving vision.” – Dr. Smith, Ophthalmologist
Regular eye exams and collaboration between healthcare providers and patients can ensure timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and comprehensive management of diabetic retinopathy. By following recommended treatment options, individuals with diabetic retinopathy can minimize vision loss and maintain optimal eye health.
Costs of Diabetic Retinopathy Treatments
Treating diabetic retinopathy can come with significant costs. The use of anti-VEGF drugs, a common treatment for the disease, can range from $1,850 to $3,200 per dose. Vitrectomy surgery, which may be necessary in advanced cases, can cost around $7,000. Laser treatments, another option for managing the condition, typically amount to approximately $2,000.
While these costs may seem daunting, it’s important to consider the long-term benefits of effective treatment. Regular screenings and early detection of diabetic retinopathy can help prevent the progression of the disease and optimize vision preservation. In the grand scheme of things, preventive screenings are cost-effective measures that can save patients thousands of dollars in future care.
To further illustrate the potential cost savings, here’s a breakdown of the average costs for the main treatment options:
| Treatment | Cost |
|---|---|
| Anti-VEGF drugs | $1,850 – $3,200 per dose |
| Vitrectomy surgery | $7,000 |
| Laser treatments | $2,000 |
As seen in the table, the costs of anti-VEGF drugs and vitrectomy surgery can be substantial. However, by focusing on early detection through regular screenings, individuals can potentially avoid the need for these high-cost treatments altogether.
Preventive screenings play a crucial role in managing diabetic retinopathy. By detecting the condition early on, healthcare providers can implement appropriate interventions and treatment plans that are both effective and cost-efficient.
In conclusion, while the costs of diabetic retinopathy treatments can be significant, investing in regular screenings and early detection is a cost-effective way to prevent further complications and preserve vision.
Ensuring Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy
Early detection is key to preventing vision loss or blindness caused by diabetic retinopathy. By undergoing regular screenings and utilizing advanced screening tests, healthcare providers can identify the disease at its earliest stages, allowing for timely treatment and the development of an effective treatment plan.
Screening tests such as retinal imaging, dilated eye exams, and fluorescein angiography have proven to be highly effective in detecting diabetic retinopathy before symptoms become noticeable. These tests provide detailed images of the retina, allowing healthcare providers to assess the extent of damage and determine the appropriate course of action.
Retinal imaging uses specialized cameras to capture high-resolution images of the retina, providing a comprehensive view of the blood vessels and structures within the eye. This enables healthcare providers to identify any abnormalities or signs of diabetic retinopathy.
Dilated eye exams involve the use of eye drops to widen the pupil, allowing for a more thorough examination of the retina. This procedure enables healthcare providers to detect early signs of the disease, such as swelling or leakage of blood vessels.
Fluorescein angiography is a diagnostic test that involves the injection of a special dye into the bloodstream. As the dye circulates through the blood vessels in the eye, healthcare providers can capture detailed images of the retina, identifying areas of leakage or blockage.
Collaboration between healthcare providers and patients is crucial in ensuring the early detection of diabetic retinopathy. By adhering to regular screenings and reporting any changes in vision or symptoms promptly, individuals with diabetes can play an active role in their eye health.
Incorporating the IRIS Solution
The IRIS solution is a comprehensive screening tool that enhances the accessibility and efficiency of diabetic retinopathy screenings. It works in conjunction with portable retinal camera systems, making it ideal for in-home evaluations and preventive screenings.
By integrating the IRIS solution into in-home healthcare practices, healthcare providers can reach diabetic patients where they are, improving access to care and ensuring that individuals receive the necessary screenings to detect and prevent diabetic retinopathy.
The IRIS solution not only enables healthcare providers to capture high-quality retinal images but also facilitates the transmission of these images for remote evaluation. This streamlines the diagnostic process, allowing for timely feedback and the development of appropriate treatment plans.
Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is achievable through regular screenings, advanced screening tests, and the utilization of innovative solutions like the IRIS solution. By prioritizing eye health and taking proactive measures, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of vision loss and maintain their overall well-being.
The IRIS Solution for In-Home Evaluations
The IRIS solution revolutionizes the way diabetic patients receive evaluations and preventive screenings in the comfort of their own homes. By leveraging portable retinal camera systems, this innovative tool facilitates in-home evaluations, improving patient care and access to healthcare providers.
With the IRIS solution, healthcare providers can meet diabetic patients where they are, eliminating the need for unnecessary travel and reducing barriers to care. This portable solution enables convenient and non-invasive diabetic retinopathy screenings, ensuring early detection and timely intervention.
By integrating the IRIS solution into in-home healthcare practices, providers can enhance patient care and close gaps in healthcare delivery. The ability to perform preventive screenings for diabetic retinopathy in the patient’s own home brings healthcare directly to their doorstep, promoting proactive disease management and reducing the risk of complications.
With the IRIS solution, healthcare providers can assess diabetic patients’ retinal health, detect potential issues, and develop personalized treatment plans. This patient-centered approach emphasizes the importance of regular screenings and comprehensive preventive care.
Benefits of the IRIS Solution:
- Convenient in-home evaluations for diabetic patients
- Improved access to healthcare providers
- Non-invasive diabetic retinopathy screenings
- Early detection and timely intervention
- Enhanced patient care and preventive management
- Closed gaps in healthcare delivery
- Promotion of proactive disease management
| IRIS Solution Features: | Benefits: |
|---|---|
| Portability | Enables in-home evaluations and screenings |
| Accuracy | Precise detection of diabetic retinopathy |
| Efficiency | Saves time and resources for both patients and healthcare providers |
| Accessibility | Improves access to diabetic retinopathy screenings |
| Non-invasiveness | Enhances patient comfort during evaluations |
The IRIS solution empowers healthcare providers to transcend traditional barriers and deliver high-quality care directly to diabetic patients. By offering in-home evaluations and preventive screenings, we can efficiently manage diabetic retinopathy and ensure the best outcomes for our patients.
With the IRIS solution, we can make a significant difference in diabetic patients’ lives, promoting proactive healthcare and preventing the devastating consequences of untreated diabetic retinopathy.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye disease that can result in vision loss if it is not addressed promptly. Understanding the four stages of the disease and the significance of early detection is critical in effectively managing it. Regular eye exams and screenings play a vital role in identifying diabetic retinopathy before irreversible damage occurs. By intervening early and implementing suitable treatment methods, we can slow down the progression of the disease, ultimately reducing the risk of vision loss and preserving overall eye health.
To mitigate the potential consequences of diabetic retinopathy, it is essential for individuals at risk to prioritize regular screenings. By actively engaging in regular screenings, we can ensure timely detection and intervention, resulting in better outcomes. Remember that diabetic retinopathy is a treatable condition, and with the right treatment strategies in place, we can prevent further vision loss and protect our eyesight.
In conclusion, the key to effective management of diabetic retinopathy lies in early detection, consistent screenings, and prompt treatment. By prioritizing regular eye exams and collaborating closely with healthcare providers, we can detect diabetic retinopathy at its early stages when treatment options are most effective. Let us remain proactive in preserving our vision and taking the necessary steps to protect our eye health.
FAQ
What is diabetic retinopathy?
What are the stages of diabetic retinopathy?
What are the common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
Who is at risk for diabetic retinopathy?
What are the costs of diabetic retinopathy treatments?
How can early detection of diabetic retinopathy be ensured?
What is the IRIS solution for diabetic retinopathy screenings?
How does diabetic retinopathy progress through the stages?
How can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
What is the importance of regular screenings for diabetic retinopathy?
Source Links
- https://retinalscreenings.com/blog/diabetic-retinopathy-stages/
- https://www.drsnyder.org/eye-care-services/eye-disease-management/diabetic-retinopathy/the-4-stages-of-diabetic-retinopathy/
- https://modernod.com/articles/2019-june/the-four-stages-of-diabeticretinopathy