Have you ever wondered what is diabetes? and how it affects your body? Many people have heard about diabetes, but understanding its definition causes, and proper care is crucial for living a healthy life. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetes, unraveling its mysteries and shedding light on the necessary steps for its management. So, let’s dive in and explore what diabetes is all about!

Key Takeaways:
- Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body regulates blood sugar levels.
- Insufficient insulin production or utilization leads to high blood sugar levels in diabetes.
- Diabetes can have a significant impact on overall health and lead to various complications if not properly managed.
- Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment.
- Proper diabetes management involves medication, lifestyle changes, and regular healthcare appointments.
Exploring the Diabetes Definition and Its Impact on Health
Diabetes is a chronic condition that significantly affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This metabolic disorder occurs when the pancreas either doesn’t produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that helps transport glucose from the bloodstream into the body’s cells for energy.
When blood sugar levels remain consistently high, it can lead to various complications and have a detrimental impact on overall health. The long-term effects of diabetes can be severe if the condition is not properly managed. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and organs over time, increasing the risk of serious health problems.
“Diabetes not only affects blood sugar control but also poses a significant risk to the cardiovascular system, kidneys, vision, and nervous system. It is crucial to understand the definition of diabetes and its impact on health to effectively manage the condition and minimize the risk of complications.”
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, including coronary artery disease and stroke. The damage to blood vessels caused by high blood sugar levels can restrict blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart, leading to cardiac issues.
Diabetes is also a leading cause of kidney disease. The kidneys’ function to filter waste products from the blood can be compromised due to high blood sugar levels, resulting in kidney damage and impaired kidney function.
Another common long-term effect of diabetes is vision loss. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can cause vision impairment and, in severe cases, blindness.
The nervous system can also be affected by diabetes, leading to diabetic neuropathy. Nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels can result in numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness, commonly in the hands and feet.
It is essential for individuals with diabetes to carefully manage their blood sugar levels, follow a healthy lifestyle, and adhere to prescribed medications to minimize the risk of these long-term complications. Regular monitoring, healthy eating habits, physical activity, and consistent healthcare appointments are key components of effective diabetes management.
What is Diabetes: Unveiling the Chronic Nature of the Disease
Diabetes is a chronic condition, meaning it is a long-term health condition that requires ongoing management. Once diagnosed, diabetes cannot be cured, but it can be effectively managed with proper care and lifestyle changes. This chronic nature of diabetes means that individuals with diabetes need to continuously monitor their blood sugar levels, take medications as prescribed, maintain a healthy diet, and engage in regular physical activity.
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but with the right tools and support, individuals can lead a fulfilling life. Daily self-care practices such as checking blood sugar levels, administering medications, and making healthy food choices are essential for maintaining optimal health. Regular physical activity is also crucial for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications.
It is important to understand that diabetes is not a condition that can be ignored or taken lightly. The chronic nature of diabetes requires a proactive approach to ensure long-term well-being. By actively managing the condition and making necessary lifestyle modifications, individuals can prevent or delay the onset of complications associated with diabetes.
Living with diabetes means adopting a mindset of self-care and taking responsibility for one’s health. It requires regular communication with healthcare professionals, adherence to medication regimens, and staying informed about new developments in diabetes management. With proper education, support, and a positive attitude, individuals with diabetes can lead a fulfilling life and minimize the impact of the condition on their overall well-being.
“Living with diabetes is a lifelong journey that requires commitment, self-discipline, and a proactive approach to health. By embracing the chronic nature of the condition and making informed choices, individuals can maintain optimal health and improve their quality of life.”
| Living with Diabetes: Key Points |
|---|
| Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. |
| Effective diabetes management includes monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity. |
| Living with diabetes involves daily self-care practices and proactive involvement in one’s health. |
| Regular communication with healthcare professionals, adherence to medication regimens, and staying informed are essential for managing diabetes effectively. |
| Living with diabetes requires a positive mindset, education, support, and a commitment to self-care. |
Identifying the Symptoms of Diabetes for Early Detection
Recognizing common diabetes symptoms is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Early intervention can help prevent complications and improve overall health outcomes. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if further evaluation for diabetes is necessary:
Recognizing Common Diabetes Symptoms
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Increased susceptibility to infections
These symptoms may occur in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although they are typically more pronounced in type 1. It is important to note that not everyone with diabetes will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity may vary between individuals.
The Subtle Signs of Prediabetes
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, prediabetes, a condition that precedes the development of diabetes, may have more subtle signs. Prediabetes is characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Some common symptoms of prediabetes include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Darkened skin patches, particularly in the armpits and neck
If you experience any of these symptoms or are at an increased risk for diabetes, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider for appropriate testing and evaluation.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you have any concerns about your health or suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of diabetes or prediabetes, it is recommended to see a doctor. It is particularly important to seek medical advice if you have a family history of diabetes, are overweight or obese, have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, or have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Early detection and proper management are key to effectively controlling diabetes and preventing complications.
Types of Diabetes: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to diabetes, it’s important to understand that there are different types, each with its own characteristics and management approaches. Let’s explore the three main types: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.

The Reality of Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that allows glucose to enter the body’s cells and be used for energy. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Living with type 1 diabetes requires diligent monitoring of blood sugar levels throughout the day. People with type 1 diabetes often use glucose meters to check their blood sugar levels and make necessary adjustments. Additionally, accurate carbohydrate counting is crucial to maintaining stable blood sugar levels, as insulin dosages are often based on the number of carbohydrates consumed.
People with type 1 diabetes need to administer insulin regularly to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. This can be done through multiple daily injections or the use of an insulin pump, which continuously delivers insulin throughout the day.
Managing Life with Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Managing type 2 diabetes involves adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes following a balanced diet that focuses on whole foods, maintaining a healthy weight through regular physical activity, and taking prescribed medications or insulin, if necessary.
In some cases, type 2 diabetes can be managed through lifestyle modifications alone, while others may require oral medications or insulin therapy to control blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to ensure treatment effectiveness and prevent complications.
Addressing Gestational Diabetes During Pregnancy
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that can pose risks to both the mother and baby. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect insulin production and utilization, leading to gestational diabetes.
Management of gestational diabetes typically involves maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity as advised by the healthcare provider, and monitoring blood sugar levels. In some cases, insulin may be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
It’s important for pregnant women with gestational diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to ensure a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications for both mother and baby.
| Type of Diabetes | Main Characteristics | Management Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | Immune system attacks pancreatic cells that produce insulin | Regular blood sugar monitoring, carb counting, insulin therapy |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production | Healthy lifestyle, diet control, physical activity, medications/insulin |
| Gestational Diabetes | Develops during pregnancy, hormonal changes affect insulin | Diet control, regular exercise, blood sugar monitoring, sometimes insulin |
Diabetes in Children

Tracing the Causes of Diabetes and Its Complex Origins

The causes of diabetes are multifactorial and involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. While some individuals have a genetic predisposition to develop diabetes, genetics alone do not determine the development of the condition. Environmental triggers and lifestyle factors also play a significant role in the onset of diabetes.
Genetic Predisposition and Environmental Triggers
Genetic predisposition refers to the increased likelihood of developing diabetes if an individual has a family history of the disease. Certain gene variants are associated with a higher risk of developing diabetes, and having close relatives with diabetes can increase the chances of developing the condition. However, genetic predisposition alone does not guarantee the development of diabetes. Environmental triggers, such as exposure to certain viruses or toxins, can activate genetic factors and contribute to the onset of the disease.
“Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers is crucial in unraveling the complex origins of diabetes.”
The Role of Lifestyle Choices in the Development of Diabetes
Lifestyle factors, including diet and physical activity, play a significant role in the development of diabetes. Unhealthy eating habits, such as consuming excessive amounts of sugar or processed foods, can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Sedentary lifestyles and lack of exercise can also impair insulin sensitivity and lead to weight gain, further exacerbating the risk of diabetes.
Implementing healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, can help prevent or manage diabetes. A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, combined with regular exercise, can support weight management, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
By understanding the complex interplay between genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices, we can gain valuable insights into the causes of diabetes. This knowledge empowers us to take proactive steps in preventing the onset of diabetes and effectively managing the condition for a healthier future.
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Options Revealed
When it comes to managing diabetes, there are various treatment options available. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. In this section, we will explore the different diabetes treatment options in detail to provide you with a comprehensive understanding.
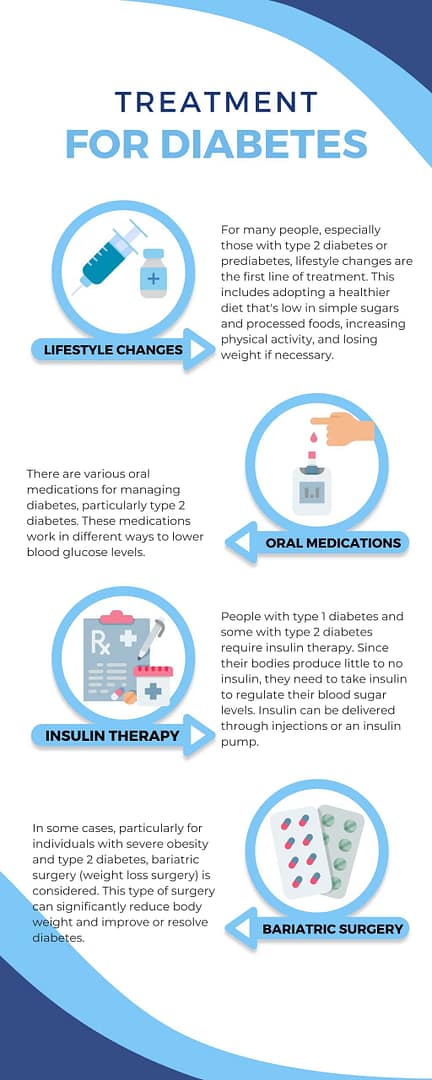
Medication and Insulin Therapy
One of the mainstays of diabetes treatment is medication. Medications are prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. There are different types of medications available, including:
- Oral Medications: These medications help the body use insulin more effectively and may be prescribed for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Common oral medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones.
- Injectable Medications: Some individuals with diabetes may require injectable medications, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors, which help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production or reducing glucose absorption.
In addition to oral and injectable medications, many individuals with diabetes require insulin therapy. Insulin therapy involves the use of insulin injections or an insulin pump to supplement insulin production in the body. Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes and may also be prescribed for those with type 2 diabetes who cannot adequately control their blood sugar levels with other medications.
Emerging Treatments and Technologies
Advancements in medical research have led to the development of emerging treatments and technologies for diabetes. These innovative approaches aim to provide better blood sugar control and improve the overall management of diabetes. Some of the emerging treatments and technologies currently being explored include:
- Artificial Pancreas: The artificial pancreas is an automated system that combines insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors to deliver insulin in a more personalized and precise manner. This technology can help individuals with diabetes achieve better blood sugar control and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Smart Insulin: Smart insulin is a promising development that aims to create insulin formulations that can adjust their activity based on blood sugar levels. This technology has the potential to simplify insulin therapy and improve treatment outcomes.
- Beta Cell Replacement: Researchers are exploring the possibilities of replacing the beta cells in the pancreas that are responsible for producing insulin. This approach could potentially provide a cure for diabetes by restoring the body’s ability to produce insulin naturally.
As these emerging treatments and technologies continue to evolve, they hold the promise of revolutionizing diabetes care and improving the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
Summary Table of Diabetes Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Type of Diabetes | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Oral Medications | Type 2 Diabetes | Improve insulin sensitivity |
| Injectable Medications | Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes | Lower blood sugar levels |
| Insulin Therapy | Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes | Supplement insulin production |
| Artificial Pancreas | Type 1 Diabetes | Automated insulin delivery |
| Smart Insulin | Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes | Adjustable insulin activity |
| Beta Cell Replacement | Type 1 Diabetes | Restore natural insulin production |
Living with Diabetes: Effective Strategies for Daily Management

Living with diabetes requires daily management and self-care. It is essential for individuals to learn how to effectively monitor their blood sugar levels, administer medications, and make healthy lifestyle choices. By adopting effective strategies for diabetes self-management, individuals can maximize their quality of life and minimize the risk of complications.
Maximizing Quality of Life with Diabetes Self-Management Education
Diabetes self-management education plays a crucial role in empowering individuals to take control of their condition. These educational programs provide valuable information on various aspects of diabetes management, including blood sugar monitoring, medication management, and healthy eating habits. By learning how to navigate the daily challenges of living with diabetes, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and achieve better blood sugar control.
Navigating Healthcare Appointments and Medication Regimens
Properly managing healthcare appointments and medication regimens is essential for individuals with diabetes. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals help monitor progress, make necessary adjustments to treatment plans, and address any concerns or complications that may arise. It is vital to communicate openly with healthcare providers, understand the purpose and dosage of prescribed medications, and follow medication schedules diligently. By actively participating in healthcare appointments and adhering to medication regimens, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes and maintain optimal health.
Adopting Preventive Measures to Thwart the Onset of Type 2 Diabetes
Preventing type 2 diabetes is possible through lifestyle modifications. Adopting a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity is also crucial for diabetes prevention, as it helps maintain a healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces the risk of developing diabetes.

The Role of Diet and Exercise in Diabetes Prevention
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in preventing type 2 diabetes. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports overall health. Avoiding sugary drinks, processed foods, and excessive consumption of added sugars can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
Regular exercise is equally important for diabetes prevention. Engaging in physical activities such as walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week can improve insulin sensitivity and lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Adding strength training exercises to the routine helps build and maintain muscle mass, which aids in metabolism and blood sugar control.
Lifestyle Change Programs and Their Success Rates
Lifestyle change programs are designed to support individuals in adopting healthy habits and preventing type 2 diabetes. These programs provide education, guidance, and ongoing support to help individuals make sustainable lifestyle changes.
Studies have shown that lifestyle change programs can be highly effective in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP), for example, demonstrated that participants who made lifestyle changes, including diet modifications and increased physical activity, reduced their risk of developing diabetes by 58%. These programs typically focus on behavior modification, goal setting, and accountability to encourage long-term adherence to healthy habits.
By prioritizing diet and exercise and participating in lifestyle change programs, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health and well-being.
Detailing Diabetes Tests and the Importance of Regular Screening
Regular screening for diabetes is important for early detection and timely intervention. It is crucial to identify diabetes at its earliest stages to prevent complications and effectively manage the condition. Diabetes tests play a significant role in diagnosing diabetes, determining prediabetes, or monitoring blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.

Diabetes tests include:
- Blood Tests: These tests measure fasting blood glucose levels, providing valuable information about an individual’s blood sugar control. They help healthcare professionals diagnose diabetes and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Regular blood testing is essential to ensure optimal diabetes management.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests: This test involves consuming a measured amount of glucose solution after fasting. Blood glucose levels are then measured at specific intervals to evaluate how well the body metabolizes glucose. It helps detect prediabetes and assess insulin resistance in individuals at risk of developing diabetes.
- Hemoglobin A1C Tests: Also known as glycated hemoglobin tests, these tests provide an average measure of blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It reflects long-term blood glucose control. Hemoglobin A1C tests are commonly used to diagnose diabetes and monitor blood sugar control in individuals with established diabetes.
Regular diabetes screening is vital for early detection, allowing for timely intervention and effective management. It enables healthcare professionals to provide personalized treatment plans, educate individuals about diabetes self-care, and lower the risk of long-term complications.
If you have risk factors for diabetes or experience symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, or fatigue, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diabetes testing and evaluation.
By prioritizing regular diabetes screening, individuals can take proactive steps towards their health and well-being by effectively managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Diabetes: Symptoms & Management

Living with diabetes has been a deeply personal journey for me. It all started a few years ago when I noticed some unusual symptoms that seemed to come out of nowhere. I was constantly thirsty, urinating more frequently, and feeling exhausted all the time. It was a confusing and scary time, but little did I know that these were the early warning signs of diabetes.
Diabetes is not just a random condition or a temporary inconvenience. It is a complex group of diseases that affects how your body uses blood sugar, or glucose, as an energy source. And let me tell you, it can have a profound impact on your life if left unmanaged.
In this article, I will delve into the symptoms of diabetes, the vital role of insulin and glucose in our bodies, the causes and risk factors, and most importantly, effective management strategies. Whether you or a loved one are dealing with diabetes, or you simply want to deepen your understanding of this condition, this article will provide you with valuable insights and support.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs of Diabetes

Diabetes is a complex condition that manifests through various symptoms, serving as early warning signs for individuals to seek medical evaluation and intervention. Understanding these symptoms is crucial in identifying the type of diabetes and determining the appropriate course of action.
Type 1 vs Type 2 vs Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
While there are symptoms common to all types of diabetes, specific symptoms are associated with each type:
| Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes | Gestational Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Gestational diabetes typically does not have noticeable symptoms. It is diagnosed through routine prenatal screenings. |
When to Consult a Doctor
If you experience any symptoms of diabetes, it is important to consult a doctor for evaluation and diagnosis. Additionally, certain risk factors should prompt a visit to the doctor, including:
- Family history of diabetes
- Obesity or weight-related issues
- Gestational diabetes during a previous pregnancy
- Persistent symptoms of diabetes
Early detection and proper management of diabetes can help prevent complications and improve overall health outcomes. If you are unsure whether your symptoms warrant a visit to the doctor, it is always better to err on the side of caution and seek professional medical advice.
The Vital Role of Insulin and Glucose in Our Bodies

Insulin and glucose play essential roles in maintaining the body’s overall functioning and energy balance. Let’s explore the significance of these two components:
Insulin: Produced by the pancreas, insulin acts as a key to unlock cells and facilitate the entry of glucose, obtained from the food we consume. This hormone helps regulate blood sugar levels and ensures that glucose can be utilized by the body’s cells for energy.
Glucose: Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for our bodies. It is derived from the carbohydrates we consume in our diet. Once insulin facilitates its entry into cells, glucose is metabolized to provide the necessary energy for various physiological functions.

In individuals with diabetes, there is a disruption in either the production or functioning of insulin, causing imbalances in blood sugar levels. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in insufficient insulin production. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body does not effectively respond to insulin. In both cases, glucose cannot efficiently enter the cells, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the bloodstream.
This imbalance of insulin and glucose can have detrimental effects on the body if not properly managed. Consistently high levels of glucose can damage various organs and systems, including the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Therefore, individuals with diabetes need to maintain appropriate blood sugar levels through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring.
In conclusion, insulin and glucose play vital roles in our bodies. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels and facilitates the entry of glucose into cells for energy production. When there is an imbalance in insulin production or function, as seen in diabetes, it can lead to elevated levels of glucose in the blood, potentially resulting in various health complications. Proper management of insulin and glucose levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
What Causes Diabetes to Develop?
The development of diabetes is influenced by various factors, both genetic and environmental. Understanding these causes is crucial in managing and preventing the condition.
Genetic and Environmental Factors in Diabetes
Genetics play a significant role in the development of diabetes. Individuals with a family history of diabetes are at a higher risk of developing the condition themselves. Specific genes related to insulin production and glucose metabolism can increase susceptibility to diabetes.
In addition to genetic factors, environmental influences also contribute to the development of diabetes. Certain viruses and toxins can trigger autoimmune responses or damage the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. Exposure to these factors can increase the likelihood of developing diabetes.
How Lifestyle and Obesity Contribute to Diabetes
Lifestyle choices, including sedentary behavior, poor diet, and obesity, are major contributors to the development of type 2 diabetes. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular physical activity can lead to insulin resistance. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it struggles to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Poor dietary choices, such as consuming excessive amounts of sugary and high-fat foods, can also contribute to the development of diabetes. These unhealthy eating habits can lead to weight gain and obesity, further increasing the risk of insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism.
Obesity, in particular, is strongly associated with the development of type 2 diabetes. Excess body weight disrupts the body’s ability to use insulin properly, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Addressing lifestyle factors, including adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, is crucial in managing and preventing diabetes.
| Causes of Diabetes | Contributing Factor |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Family history of diabetes |
| Specific genes associated with insulin production and glucose metabolism | |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to certain viruses and toxins |
| Lifestyle Choices | Sedentary behavior and lack of physical activity |
| Poor diet, high in sugar and fat | |
| Obesity |
Does Diabetes Mean Sugar Is Off-Limits?
It is a common misconception that people with diabetes must completely avoid sugar. While it is important to monitor sugar intake, it does not mean that sugar is off-limits. The key is to consume sugar in moderation and be mindful of overall carbohydrate intake.
Understanding the Relationship Between Sugar and Diabetes
In individuals with diabetes, the body has difficulty regulating blood sugar levels. Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can cause blood sugar levels to spike, leading to potential health complications. However, it’s important to note that sugar is not the sole culprit in the development or management of diabetes. Carbohydrates, which include sugar, are the main source of energy for the body, and they can be consumed in a balanced and controlled manner.
What Foods to Avoid if You Are Diabetic?
In addition to monitoring sugar intake, individuals with diabetes should also be cautious about consuming foods that can significantly affect blood sugar levels. Some foods to avoid or limit include:
- Highly processed sugars, such as table sugar, candy, and sugary beverages
- Refined carbohydrates, including white bread, white rice, and pastries
- Saturated and trans fats, found in fried foods and commercially baked goods
- Sweetened snacks, such as cookies, cakes, and sugary cereals
- Sugary condiments, like ketchup, barbecue sauce, and salad dressings
It is important to consult a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to create a personalized meal plan that takes into consideration individual dietary preferences and needs. They can provide guidance on making healthy food choices, managing carbohydrate intake, and incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into your diet.
| Foods to Avoid for Diabetics: |
|---|
| Highly processed sugars: table sugar, candy, sugary beverages |
| Refined carbohydrates: white bread, white rice, pastries |
| Saturated and trans fats: fried foods, commercially baked goods |
| Sweetened snacks: cookies, cakes, sugary cereals |
| Sugary condiments: ketchup, barbecue sauce, salad dressings |
Diagnosis: How Common Is Diabetes and Who Is at Risk?
Diabetes is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence varies among different demographics, with certain populations being at a higher risk. Several risk factors contribute to the development of diabetes, including age, family history, obesity, and race/ethnicity. Additionally, genetic factors play a role in the predisposition to diabetes. Understanding the demographics, prevalence, and risk factors associated with diabetes can facilitate the identification of individuals at higher risk. This knowledge enables healthcare providers to implement preventative measures and early intervention strategies to reduce the incidence and impact of diabetes.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Effects of Diabetes
Diabetes, if not properly managed, can lead to various complications and long-term effects. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prioritize their health and work closely with their healthcare team to prevent or manage these complications. Here are some of the potential complications and long-term effects of diabetes:
- Heart disease: Diabetes increases the risk of developing heart disease, including conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure.
- Stroke: People with diabetes have a higher risk of experiencing strokes, which can cause significant physical and cognitive impairments.
- Kidney disease: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease and the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, leading to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. This can result in pain, numbness, and tingling in the hands and feet.
- Eye damage: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can cause vision loss or even blindness.
- Foot complications: Diabetes can affect the circulation and nerve function in the feet, increasing the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation.
- Skin conditions: Diabetes can make the skin more susceptible to infections and slow-healing wounds.
- Hearing impairment: Studies have shown a higher prevalence of hearing loss among individuals with diabetes.
- Increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease: Some studies have suggested a link between diabetes and an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
To reduce the risk of these complications and long-term effects, individuals with diabetes should maintain good blood sugar control, manage their blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and adopt a healthy lifestyle. Regular monitoring, medication management, and lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular physical activity, can help prevent or delay the onset of these complications and improve overall well-being.
| Complication/Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart disease | Increased risk of coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure. |
| Stroke | Higher risk of experiencing strokes, which can cause physical and cognitive impairments. |
| Kidney disease | Damage to the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease and the need for dialysis or transplantation. |
| Nerve damage | High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, resulting in pain, numbness, and tingling. |
| Eye damage | Damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss or blindness. |
| Foot complications | Risk of foot ulcers, infections, and amputation due to poor circulation and nerve function in the feet. |
| Skin conditions | Increased susceptibility to skin infections and slow-healing wounds. |
| Hearing impairment | Higher prevalence of hearing loss among individuals with diabetes. |
| Increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease | Possible link between diabetes and an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. |
Effective Management and Treatment Strategies for Diabetes
Comprehensive management and treatment strategies are essential for effectively managing diabetes. The key components of diabetes management include monitoring blood sugar levels, using medication as prescribed, and making necessary lifestyle changes.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels and Using Medication
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes. By tracking changes in blood sugar levels, individuals can make necessary adjustments to their medication dosage, meal planning, and physical activity. This helps ensure that blood sugar levels are kept within a target range and reduces the risk of complications associated with high or low blood sugar.
Diabetes medication plays a critical role in managing blood sugar levels. Depending on the type of diabetes, individuals may be prescribed insulin, oral medications, or other injectable medications. Insulin is typically required for individuals with type 1 diabetes, while those with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed oral medications or a combination of medications. It is important to take medication as prescribed and to be aware of potential side effects or interactions.
Lifestyle Changes: Diet, Exercise, and Weight Control
Lifestyle changes are an essential part of diabetes management. Adopting a healthy diet that is rich in nutrients, low in sugar and unhealthy fats, and well-balanced can help regulate blood sugar levels. A registered dietitian can provide guidance on meal planning and help create a personalized eating plan that takes individual preferences and needs into account.
Engaging in regular physical activity is also crucial for managing diabetes. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to effectively use glucose for energy. It can also help with weight management and overall cardiovascular health. A healthcare provider can provide recommendations on suitable exercise routines based on individual abilities and preferences.
Weight control is particularly important for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those who are overweight or obese. Losing excess weight can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. A combination of a healthy diet and regular physical activity can contribute to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
| Management Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring | Tracking blood sugar levels to make necessary adjustments to medication and lifestyle. |
| Medication | Taking prescribed diabetes medications, such as insulin or oral medications, as directed. |
| Healthy Diet | Adopting a balanced diet that is low in sugar and unhealthy fats, and high in nutrients. |
| Regular Exercise | Engaging in physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and overall health. |
| Weight Control | Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise. |
Preventing Diabetes Through Healthy Habits

Adopting healthy habits is crucial in preventing or delaying the onset of diabetes. By maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and getting regular check-ups, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes.
Can Stress Cause Diabetes and How Can You Reduce Risks?
While stress itself does not directly cause diabetes, it can contribute to certain risk factors associated with the condition. Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating, sedentary lifestyle choices, and poor sleep habits, all of which can increase the risk of developing diabetes. To reduce the risk, it is important to manage stress effectively.
This can be achieved through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Engaging in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and seeking support from friends, family, or professionals can also help in reducing stress levels.
What Are the Stages of Diabetes and Can They Be Prevented?
Understanding the stages of diabetes, particularly prediabetes can provide an opportunity for early intervention and prevention strategies. Prediabetes occurs when blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. By identifying prediabetes, individuals can make lifestyle changes that can prevent or delay the progression to full-blown diabetes.
This includes adopting healthy eating habits, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help monitor blood sugar levels and identify any potential risks or warning signs of diabetes. Early intervention and preventive measures are key in managing the risk and preventing diabetes.
By implementing healthy habits, managing stress, and understanding the stages of diabetes, individuals can reduce their chances of developing diabetes and improve their overall health outcomes. Prevention is always better than treatment, and by taking proactive steps, we can lead a healthier and diabetes-free life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing diabetes is vital for individuals to maintain their overall health and well-being. Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing care and attention. It involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups to ensure optimal blood sugar control and minimize the risk of complications.
Early detection plays a crucial role in effective diabetes management. Regular screenings and recognizing the common symptoms of diabetes can lead to timely intervention and appropriate treatment. By taking proactive measures, individuals can prevent further health complications and maintain a higher quality of life.
Living with diabetes may present challenges, but with the right support and knowledge, individuals can successfully navigate their daily routines. Diabetes self-management education programs provide valuable guidance and resources to empower individuals to take control of their condition. Incorporating a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication adherence are key components of effective management.
Overall, understanding diabetes, its causes, and available treatment options allows individuals to make informed decisions and take proactive steps toward their health. By staying diligent in their management strategies and seeking regular medical care, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the impact of this chronic condition.

Sources
For those looking to understand and manage diabetes, several resources can provide valuable information and support:
- Diabetes UK offers a wealth of resources including educational materials for people with Type 2 diabetes, innovative online self-management programs, and guides for healthcare professionals on diabetes self-management education (DSME).
- The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)emphasizes the importance of physical activity and proper medication management in diabetes care. They provide resources on how to incorporate physical activities into daily routines, how to manage medications effectively, and guidance on blood glucose monitoring.
- The American Diabetes Association (ADA), through its Diabetes Care journal, highlights the impact of diabetes self-management education and support (DSMES) on the use of healthcare services and adherence to treatment recommendations. They also discuss the importance of nutrition therapy in diabetes management and the role of registered dietitians in providing diabetes-specific medical nutrition therapy (MNT).
- Healthy People 2030 lists evidence-based resources that cover a range of topics including the screening for diabetes, team-based care, and interventions engaging community health workers. They offer a comprehensive overview of diabetes objectives and data, tools for action, and a multitude of related resources.
These resources can help individuals with diabetes, their families, and healthcare professionals to gain a better understanding of the condition, learn about the latest treatments and management strategies, and find support for daily living with diabetes.
For more information, assistance, or to share your experiences and questions about diabetes management, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
We value your input and are here to support you on your journey with diabetes. You can contact us through our website’s contact form, or send us an email. Our dedicated team is committed to providing you with the resources and guidance you need to manage your diabetes effectively.
